Ultrathin 2D cuprate with active periodic copper single sites, a new catalyst for Chan-lam coupling
![The illustration of anion exchange strategy for the top-down exfoliation of bulk cuprate materials [Cu<sub>4</sub>(OH)<sub>6</sub>][O<sub>3</sub>S(CH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>4</sub>SO<sub>3</sub>] into atomically thin 2D-CuSSs and Atomic model of 2D-CuSSs. Credit: Science China Press Ultrathin 2D cuprate with active periodic copper single sites, a new catalyst for Chan-lam coupling](https://scx1.b-cdn.net/csz/news/800a/2022/ultrathin-2d-cuprate-w.jpg)
This study is led by Dr. Lu Jiong from National University of Singapore (NUS), in collaboration with Dr. Koh Ming Joo (NUS), Dr. Chun Zhang (NUS) and Dr. Honghan Fei from (Tongji University). This team has devised a ligand exchange strategy to exfoliate bulk cuprate crystals into atomically thin 2D cuprate layers whose basal plane contains periodic arrays of accessible unsaturated Cu(II) single sites (2D-CuSSs). Because of their unique structure, these 2D-CuSSs are found to catalyze efficient Chan-Lam coupling. This work was published in National Science Review last month.
Copper-catalyzed Chan-Lam coupling is a key oxidative coupling process that is extensively used in organic synthesis for the production of pharmaceutically important aryl carbon-heteroatom compounds. Compared to homogeneous catalysts for Chan-Lam coupling, heterogeneous ones are much less explored even though they are arguably more attractive in the chemical industry due to their easier separation and recycling. Although a number of heterogeneous Cu catalysts have been reported for this reaction, problems such as low stability and/or metal leaching are common.
“2D-CuSSs synthesized here contain a high density of accessible coordinatively unsaturated single Cu site arrays in 2D cuprate layer, which ensure them serve as efficient and robust heterogeneous catalyst candidates for cross-coupling reactions,” Lu Jiong says.
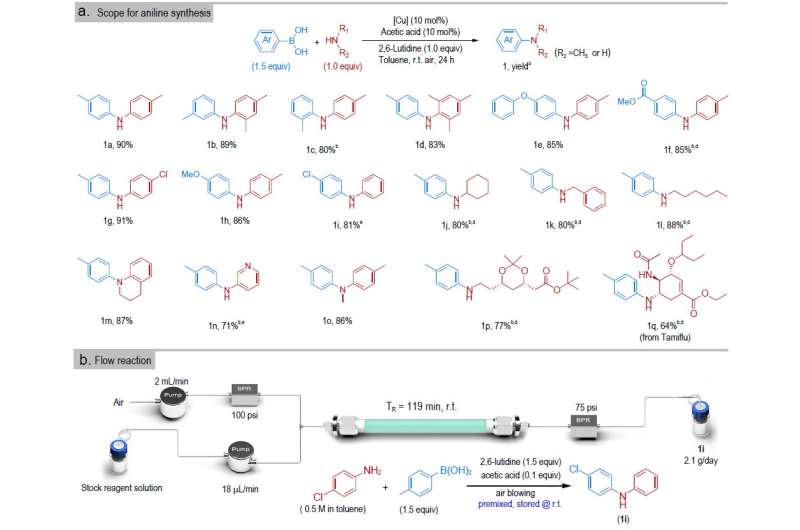
The team tested a series of substituted anilines and boronic acids to examine the substrate scope of the C-N coupling catalyzed by 2D-CuSSs and demonstrated distinct advantages of 2D-CuSSs over traditional homogeneous counterparts. This can be attributed to the large open surface of 2D-CuSSs with abundance of undercoordinated Cu single sites.
The presence of atomically well-defined active sites also allows us to explore the structure-performance relationships and to gain molecular-level insights into the reaction mechanism as revealed by both operando experimental and theoretical studies. Overall, the robust stability in both batch and continuous flow reactions, coupled with their good catalytic performance in the preparation of complex amine and ether compounds underscore the potential applicability of 2D-CuSSs in fine chemical synthesis.
Nickel-catalyzed cross-coupling of aromatic ethers proceeds via a nickelate anion
Huimin Yang et al, Catalytically Active Atomically Thin Cuprate with Periodic Cu Single Sites, National Science Review (2022). DOI: 10.1093/nsr/nwac100
Citation:
Ultrathin 2D cuprate with active periodic copper single sites, a new catalyst for Chan-lam coupling (2022, August 4)
retrieved 4 August 2022
from https://phys.org/news/2022-08-ultrathin-2d-cuprate-periodic-copper.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
For all the latest Science News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

