Tuning local coordination of catalysts for better lithium-sulfur batteries
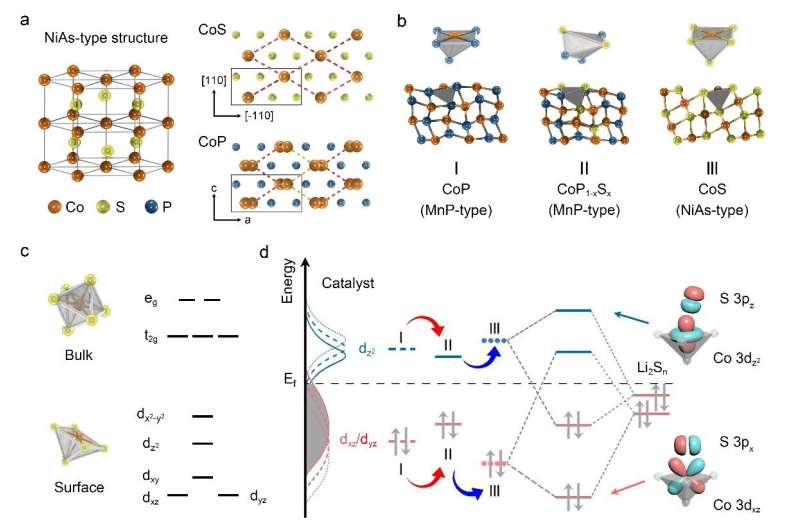
A research team led by Prof. Zhu Qingshan from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences investigated the electronic structure transition from NiAs- to MnP- type CoPxS1-x compounds and how the transition influences catalytic activity of polysulfide conversion reactions in lithium-sulfur batteries.
The study was published in ACS Nano on Jan. 30.
Lithium-sulfur batteries are promising energy storage systems due to their high theoretic capacity and specific energy. However, polysulfide shuttling leads to the decay of batteries, limiting their practical applications.
Catalysts can accelerate the conversion of polysulfides and relatively suppress the shuttling, which serves as the effective approach to improving cyclability of Li-S batteries. The lack of understanding of the catalytic mechanism and origin poses an obstacle to the design of Li-S catalysts.
“Compared with NiAs, cations in MnP-type compounds shift along the plane vertical to c-axis, leading to the shortened inter-center distance of two-edge polyhedra and enhancing the metal-metal bonding,” said Zhang Huigang, a principal investigator at IPE. Their electronic structures changed with the coordinated polyhedra. The resultant upshift or downshift of d-band would determine the bonding of catalysts and polysulfides.
“By tuning the coordination structure of active centers and optimizing the d-orbitals, we can design catalysts more rationally,” said Prof. Zhu.
Based on the transition, the researchers doped CoP with sulfur and distorted the [CoP6] polyhedra to shift the cation centers. As a result, the dz2 orbital shifted down and the dxz/dyz orbital moved up, enhancing the bonding toward polysulfides.
To realize practical applications of high-loading Li-S batteries, they electrospun CoPxS1-x inside porous carbon nanofibers, forming chain-like nanoreactors, which confined and effectively catalyzed the polysulfide conversion reaction.
“The catalyst design and nanofiber construction enable excellent cyclability of high-loading Li-S batteries,” said Zhang.
More information:
Zihan Shen et al, Tuning the Local Coordination of CoP1–xSx between NiAs- and MnP-Type Structures to Catalyze Lithium–Sulfur Batteries, ACS Nano (2023). DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.2c12436
Citation:
Tuning local coordination of catalysts for better lithium-sulfur batteries (2023, February 9)
retrieved 10 February 2023
from https://phys.org/news/2023-02-tuning-local-catalysts-lithium-sulfur-batteries.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
For all the latest Science News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

