The strength of new tools in microbiome studies lies in their combined and integrated use
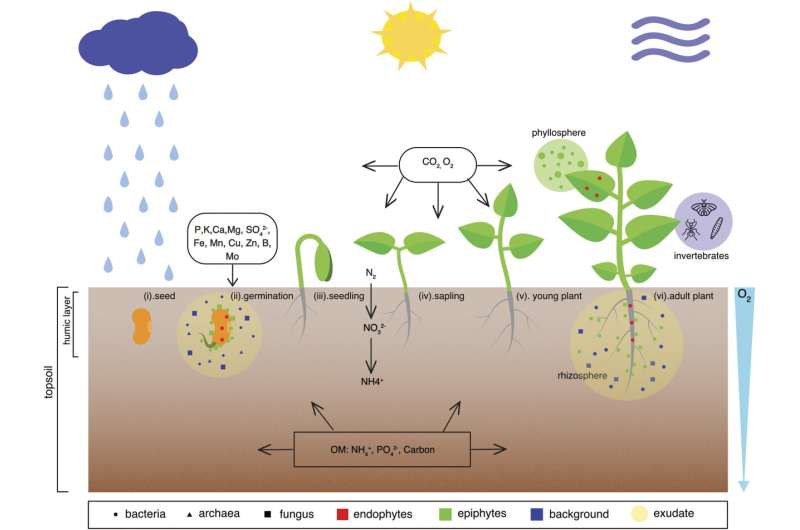
Technology is rapidly evolving across many disciplines. Ground-breaking results are often obtained when new technology enables novel approaches or when technologies are transferred from other fields of research. In a recent review article, Dr. Esther Singer and colleagues explored novel and emerging technologies in relation to plant microbiome research.
“Plant root microbiome research has the potential to play an enormous role in improving food and energy security,” explained Singer, the lead author on the paper and a scientist at the Joint Genome Institute and the Lawrence Berkley National Laboratory in Berkley, California. “With the onset of new technologies to collect and process data, we hope to further disclose the drivers and complex underground interactions that determine the health of entire soil ecosystems. Healthy soils make healthy humans.”
Singer and her colleagues describe how exciting new technologies can be applied to plant microbiome research to develop a broader understanding of soil ecosystem health and climate research. For example, scientists can combine mesocosms (controlled enclosures that strive to bridge the gap between the lab and the real world) with in situ sensors and imaging tools that collect soil and plant trait data. The controlled nature of this platform allows for replicable experimentation on relevant spatial and temporal scales.
“Another example is the use of novel computational data processing and analysis methods that can facilitate the identification of underlying drivers and interactions when complex and multi-disciplinary datasets are collected,” Singer said. “The availability and development of novel and emerging technologies in plant root microbiome research will make impacts in a number of fields, including agriculture, climate change research and mitigation, environmental conservation, and bioremediation. The strength of applying these tools will lie in their combined and integrated use.”
The review discusses the strengths and limitations of many novel and emerging technologies, including imaging tools, robotics, and molecular analyses, experimental platforms from micro- to mesocosms, and data integration, modeling, and prediction tools. It is meant to give researchers an overview of emerging instrumentation and methods, and to stimulate discussion and brainstorming about how to integrate these into their future studies to help make the world more sustainable.
Underneath it all: Dishing the dirt on protists
Esther Singer et al, Novel and Emerging Capabilities that Can Provide a Holistic Understanding of the Plant Root Microbiome, Phytobiomes Journal (2021). DOI: 10.1094/PBIOMES-05-20-0042-RVW
Provided by
American Phytopathological Society
Citation:
The strength of new tools in microbiome studies lies in their combined and integrated use (2021, August 25)
retrieved 25 August 2021
from https://phys.org/news/2021-08-strength-tools-microbiome-lies-combined.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
For all the latest Science News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

