TESS discovers new warm brown dwarf
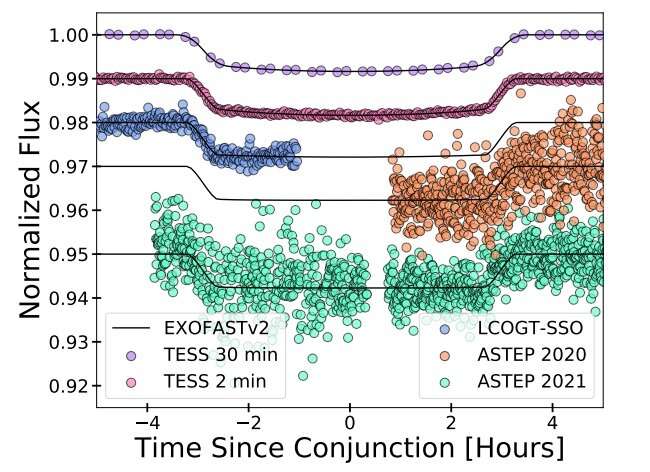
Using NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), an international team of astronomers has detected a new warm brown dwarf. The newfound object, designated HIP 33609 b, transits a bright and rapidly rotating star. The discovery was presented in a paper published January 23 on the arXiv pre-print repository.
Brown dwarfs (BDs) are intermediate objects between planets and stars, occupying the mass range between 13 and 80 Jupiter masses (0.012 and 0.076 solar masses). Although many brown dwarfs have been detected to date, such objects orbiting other stars are a rare find.
Recently, a group of astronomers led by Noah Vowell of the Michigan State University, has found a new object of this rare type. The report that a transit signal has been identified in the light curve of a B-star known as HIP 33609. Follow-up spectroscopic and photometric observations confirmed that the transiting object is a large, massive and warm brown dwarf.
“In this paper, we present the discovery of a benchmark transiting BD in the HIP 33609 system. We use a combination of spectroscopic and photometric observations from both ground- and space-based facilities in order to characterize the host star and transiting BD,” the researchers explained.
The newly found brown dwarf is inflated as its radius is about 58% larger than Jupiter, while its mass is estimated to be some 68 Jupiter masses. The observations show that the orbit of HIP 33609 b is highly eccentric, with an eccentricity of 0.56, and the orbital period was measured to be 39.47 days. The brown dwarf’s equilibrium temperature was found to be 1,237 K.
The star HIP 33609 has a radius of about 1.86 solar radii and is 2.38 times more massive than the sun. It is a fast rotator as its rotation period was measured to be approximately 55.6 km/s. The star’s effective temperature is about 10,400 K.
The astronomers noted the unusual parameters of HIP 33609 b, especially its long orbital period, could help advance our knowledge of transiting companions around hot stars. Therefore, HIP 33609 b is perceived as a benchmark for substellar evolutionary models. They added that all previously discovered transiting companions around B- and A-type stars have orbital periods less than 10 days.
“The HIP 33609 system is an ideal candidate for testing substellar evolutionary models, as well as for a comparative analysis relative to the extensive population of highly irradiated, short period BDs and giant planets,” the authors of the paper wrote.
Additionally, the observations conducted by Vowell’s team resulted in a young stellar association (estimated to be about 150 million years old), which received designation MELANGE-6. It appears that HIP 33609 is a member of this association.
More information:
Noah Vowell et al, HIP 33609 b: An Eccentric Brown Dwarf Transiting a V=7.3 Rapidly Rotating B-Star, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2301.09663
© 2023 Science X Network
Citation:
TESS discovers new warm brown dwarf (2023, February 1)
retrieved 1 February 2023
from https://phys.org/news/2023-02-tess-brown-dwarf.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
For all the latest Science News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

