Swimmer’s Itch: What causes this neglected snail-borne disease?
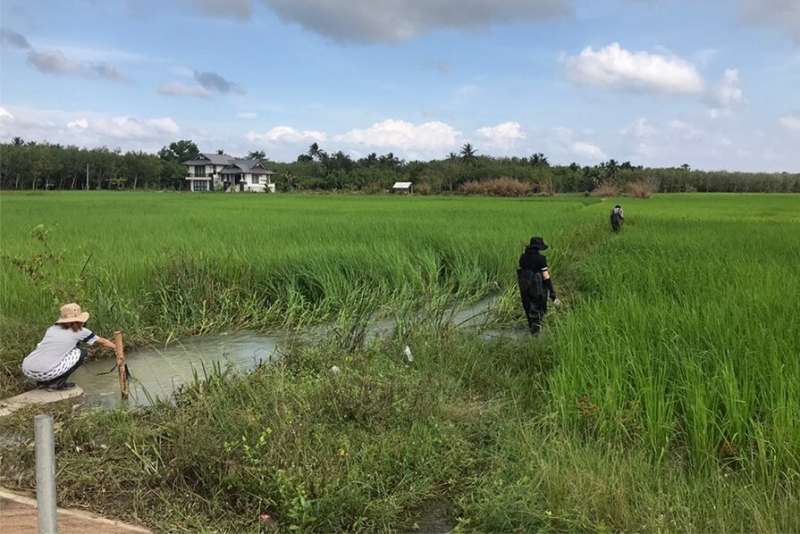

Cercarial dermatitis, also known as swimmer’s itch or clam-digger’s itch, is caused by the larvae of blood flukes that are parasites of birds or mammals. When these larvae, called cercariae, penetrate human skin, they trigger an allergic reaction within 10-15 hours that takes about a week to heal. Unable to mature into adults, the larvae then die on the skin. The gravity of an outbreak depends on how humans and birds or mammals come in contract with the aquatic environment, but people engaged in water activities, such as farmers, fishermen, and agricultural workers, are most likely to be affected.
Between August and October 2020, a cercarial dermatitis outbreak with 359 confirmed cases occurred in Chana district, Songkhla Province, South Thailand. It mostly affected rice farmers from the area, who were busy with cultivation during the rainy season. Following a short investigation, three cases of patients were confirmed to be cercarial infections by skin biopsy (Bureau of Epidemiology, Department of Disease Control, Ministry of Public Health, Thailand).
“The study of intermediate host and definitive host in the outbreak area are important for the control program of snail-borne disease,” the researchers argue in their research paper, which was published in the open-access scientific journal Evolutionary Systematics.
Having studied six snail species from the area, they found out that two were infected, each with three different species of flatworms. The cercarial dermatitis outbreak was due to ruminant parasites, such as the blood fluke Schistosoma indicum, which often uses domestic animals as its host.
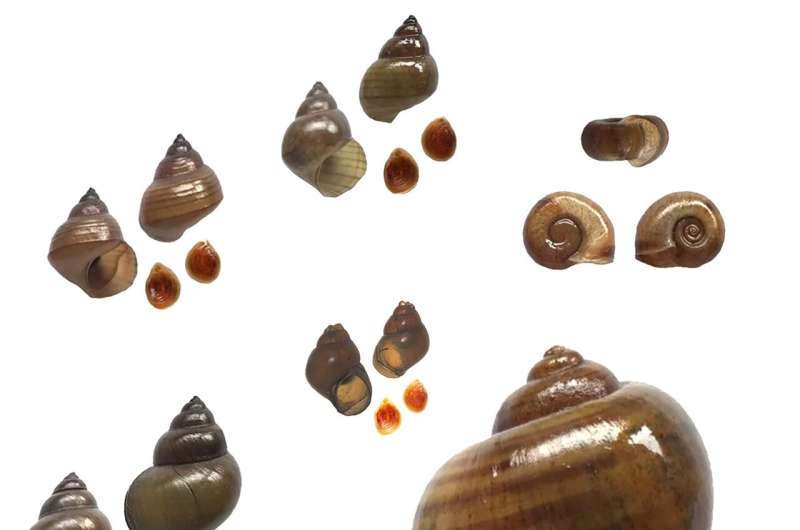

“Ruminant-infecting trematodes, namely, S. indicum and S. spindale, cause a hepato-intestinal schistosomiasis resulting in reduced milk yield,” the authors explain. “This occurrence of S. indicum and S. spindale implies the spread of cattle blood fluke cercariae in aquatic environments.”
“Additionally, these species of the S. indicum group primarily cause cercarial dermatitis in humans, which has become an important public health issue for people living in endemic regions.”
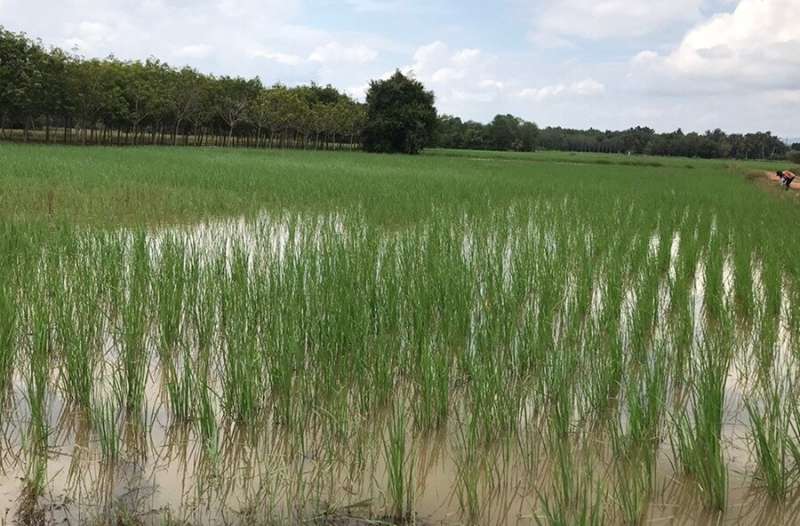

“In South India and Southeast Asia, where S. indicum and S. spindale have been reported to be widespread, they caused major pathology and mortality to livestock, leading to welfare and socio-economic issues, predominantly among poor subsistence farmers and their families.”
Some of the other worm species they found parasitized the intestines of fish, mammals, or birds, while others caused anemia and even death in ruminant animals.
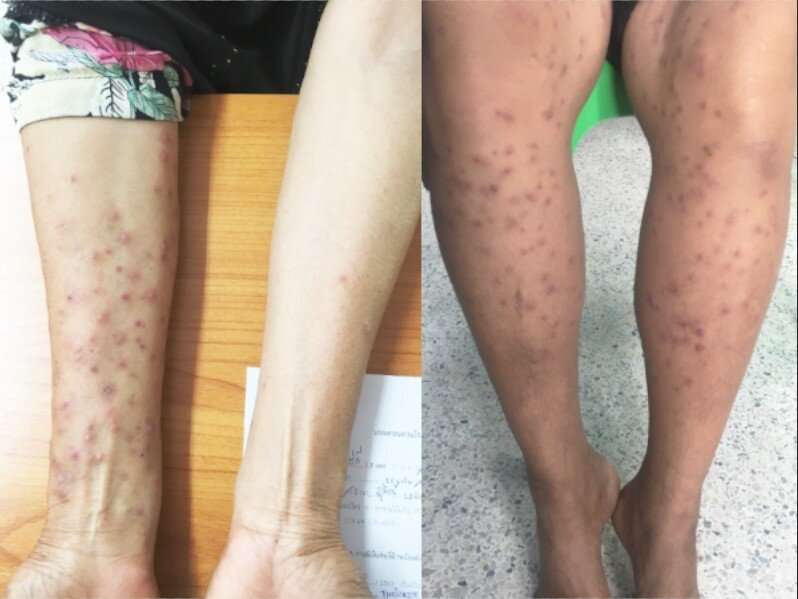
“The results of this study will provide insights into the parasite species that cause cercarial dermatitis and may improve our understanding of public health problems in the outbreak and agricultural vicinity areas,” the authors of the study say. “In addition, the sequence data generated here are the first S. indicum DNA sequences from Thailand, which will be useful for further genetic study of the other blood flukes in this region.”
Agents of food-borne zoonoses confirmed to parasitise newly-recorded in Thailand snails
Duangduen Krailas et al, Cercarial dermatitis outbreak caused by ruminant parasite with intermediate snail host: schistosome in Chana, South Thailand, Evolutionary Systematics (2022). DOI: 10.3897/evolsyst.6.87670
Citation:
Swimmer’s Itch: What causes this neglected snail-borne disease? (2022, September 14)
retrieved 14 September 2022
from https://phys.org/news/2022-09-swimmer-neglected-snail-borne-disease.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
For all the latest Science News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

