Scientists serendipitously discover rare cluster compound
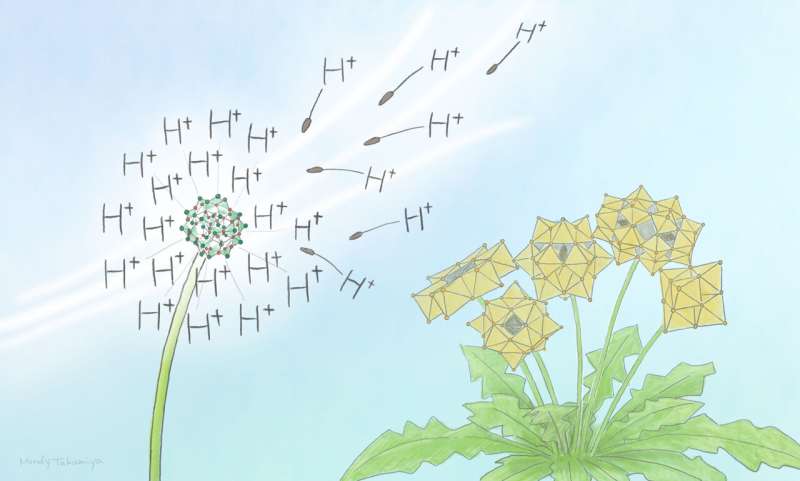
Scientists at Kyoto University’s Institute for Cell-Material Sciences have discovered a novel cluster compound that could prove useful as a catalyst. Compounds, called polyoxometalates, that contain a large metal-oxide cluster carry a negative charge. They are found everywhere, from anti-viral medicines to rechargeable batteries and flash memory devices.
The new cluster compound is a hydroxy-iodide (HSbOI) and is unusual, as it has large, positively charged clusters. Only a handful of such positively charged cluster compounds have been found and studied.
“In science, the discovery of new material or molecule can create a new science,” says Kyoto University chemist Hiroshi Kageyama. “I believe that these new positively charged clusters have great potential.”
The first metal oxide cluster was discovered in 1826. Chemists have since synthesized hundreds of compounds with negatively charged clusters, which have properties useful in magnetism, catalysis, ionic conduction, biological applications and quantum information. Their properties make them useful in diverse fields from catalysis to medicine and chemical synthesis.
In more recent years, scientists have focused their attention on synthesizing compounds with positively charged clusters and learning their properties.
Kageyama and his colleague Ryu Abe found their positive cluster by accident. Since 2016, the two scientists—Kageyama, a solid-state chemist and Abe, a catalytic chemist—have been on a quest to develop new compounds that can absorb visible light for photocatalysis. They were studying a chlorine-containing (Sb4O5Cl2) compound and trying to replace the chlorine atom with iodine.
“However, a new material that was completely different from what we expected was obtained accidentally,” says Kageyama.
What the scientists expected was a material that contains 22 atoms in the unit cell. What they got instead was a compound that contains 800 atoms in its unit cell.
At the beginning, the scientists could not unravel the chemical’s structure. A traditional technique called powder X-ray diffraction failed when faced with the material’s complexity. After a year, Kageyama thought he could use three-dimensional electron tomography, a cutting-edge electron microscopy technique that has attracted recent attention as a tool to image the structure of proteins. The scientists approached Artem Abakumov and Joke Hadermann at University of Antwerp, Belgium, to work on the structure. And when their collaborators sent the data back, the scientists were thrilled to see large clusters.
Further lab work showed the hydroxyiodide molecule contained acidic protons, which is important in catalysis.
“This finding may open up new possibilities in the design of solid-state catalysts,” says Kageyama.
Their work will be published in Science Advances.
Yuki Watanabe et al, Polyoxocationic antimony oxide cluster with acidic protons, Science Advances (2022). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abm5379. www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abm5379
Citation:
Scientists serendipitously discover rare cluster compound (2022, June 17)
retrieved 17 June 2022
from https://phys.org/news/2022-06-scientists-serendipitously-rare-cluster-compound.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
For all the latest Science News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

