Scientists discover how Golden staph hides and thrives in human cells using state-of-the-art research tool
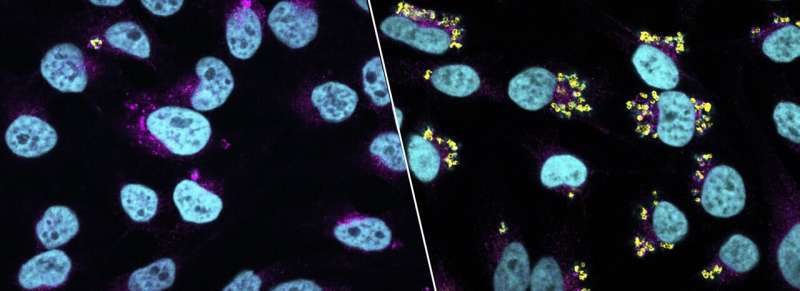
Researchers have discovered how Golden staph, a common bug that can cause one of the most serious bacterial infections, hides inside human cells to avoid detection by the immune system.
Nearly one in three people globally unknowingly carries Golden staph, or Staphylococcus aureus, in their nose or on their skin. While the bacterium is harmless to most, it can lead to serious infection and even death if it enters the bloodstream through a cut, surgical wound or catheter.
The breakthrough, led by the University of Melbourne’s Dr. Abdou Hachani, a Senior Researcher at the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute) and published in eLife, was made possible by a new state-of-the-art methodology called “InToxSa.” It enables the study of Golden staph behavior inside human cells on a large scale, with greater efficiency and speed, ultimately accelerating the research process.
Dr. Hachani explained that the innovative approach, developed by his research team, is key to understanding how Golden staph behaves inside cells and gaining valuable knowledge about the bacteria’s ability to survive and thrive in humans.
“We tested hundreds of S. aureus strains taken from patients with bloodstream infections using InToxSa, and observed specific changes that make the bacteria less harmful and better at surviving in our bodies,” said Dr. Hachani.
“We identified the genes that control the bacteria’s ability to persist inside host cells without killing them. This is an important advance to understand how S. aureus can cause lethal infections.”
University of Melbourne’s Professor Tim Stinear, Molecular Microbiologist at the Doherty Institute, explained that the outputs of the platform will guide and inform precision and predictive medicine to treat complicated infections based on the genetic make-up of Golden staph clinical samples.
“InToxSa is a powerful tool that combines genetic analysis, microbiological data and statistical comparisons. It can handle a large volume of data in a systematic and standardized way, which eventually leads to more comprehensive and accelerated scientific discoveries—like ours,” said Professor Stinear.
“Using this platform, we were able to identify mutations in the bacteria that are clinically relevant and promote their ability to persist inside the body. This new knowledge will guide research to find new ways to combat these infections.”
More information:
Abderrahman Hachani et al, A high-throughput cytotoxicity screening platform reveals agr-independent mutations in bacteraemia-associated Staphylococcus aureus that promote intracellular persistence, eLife (2023). DOI: 10.7554/eLife.84778
Provided by
The Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity
Citation:
Scientists discover how Golden staph hides and thrives in human cells using state-of-the-art research tool (2023, June 15)
retrieved 15 June 2023
from https://phys.org/news/2023-06-scientists-golden-staph-human-cells.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
For all the latest Science News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

