PDGFR kinase inhibitor found to protect against septic death via regulation of BTLA
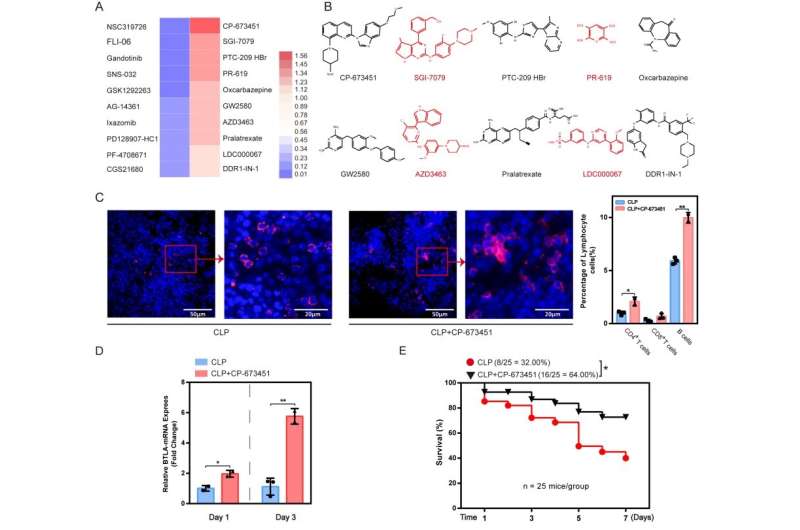
In a study was led by Dr. Jianxin Jiang (Institute of Department of Trauma Medical Center, Daping Hospital, State Key Laboratory of Trauma, Burns and Combined Injury, Army Medical University), a team screened a highly selective kinase inhibitor library and found that CP-673451 can upregulate BTLA expression on immunocytes and reduce sepsis-related mortality.
The team also found that CP-673451 treatment mainly enhanced BTLA expression in CD4+ T, CD8+ T cells and B cells. CP-673451 treatment was associated with reduced sepsis-induced lung injury such as infiltration of inflammatory cells and thickened alveolar septa were significantly reduced.
CP-673451 administration can significantly reduce enzyme release in the heart, kidney and liver in septic mice. Furthermore, CP-673451 administration also reduced immune cell apoptosis. In conclusion, CP-673451 might reduce the mortality rate of septic mice by protecting the function of vital organs and reducing the apoptosis of immune cells.
To further elucidate the mechanism by which CP-673451 reduces mortality in sepsis, the researchers observed its effect on cytokine release. The serum concentration of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α decreased significantly after CP-673451 treatment in septic mice. Furthermore, the release of chemokines, such as CCL1, CCL2, CCL7 and CXCL13, was also reduced significantly after treatment with CP-673451 in septic mice.
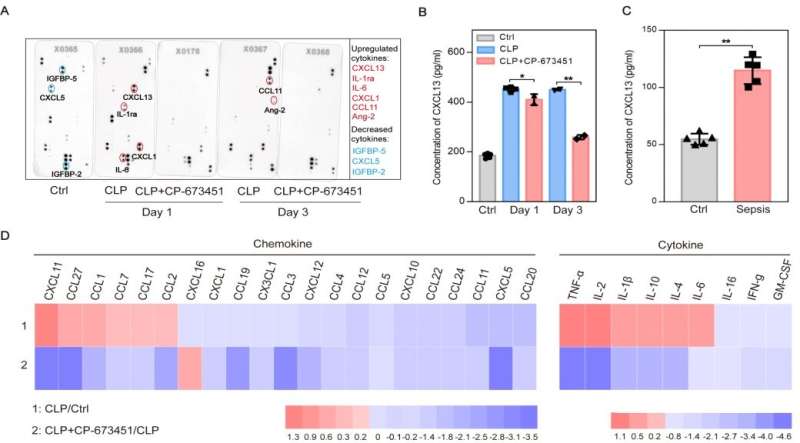
These results suggested that the selective PDGFR kinase inhibitor CP-673451 might inhibit the chemotaxis of T and B cells by inhibiting the release of chemokines such as CXCL13, CCL1, CCL2 and CCL7, thus reducing the release of cytokines by the two groups of immune cells to the peripheral blood. Consequently, CP-673451 alleviated the cytokine storm and decreased the mortality of sepsis. Therefore, the study provided a new therapeutic target and a new effective compound for sepsis.
The research was published in Science China Life Sciences.
Qiang Wang et al, PDGFR kinase inhibitor protects against septic death via regulation of BTLA, Science China Life Sciences (2022). DOI: 10.1007/s11427-021-2136-y
Citation:
PDGFR kinase inhibitor found to protect against septic death via regulation of BTLA (2022, September 15)
retrieved 16 September 2022
from https://phys.org/news/2022-09-pdgfr-kinase-inhibitor-septic-death.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
For all the latest Science News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

