Pass the salt: This space rock holds clues as to how Earth got its water

Sodium chloride, better known as table salt, isn’t exactly the type of mineral that captures the imagination of scientists. However, a smattering of tiny salt crystals discovered in a sample from an asteroid has researchers at the University of Arizona Lunar and Planetary Laboratory excited, because these crystals can only have formed in the presence of liquid water.
Even more intriguing, according to the research team, is the fact that the sample comes from an S-type asteroid, a category known to mostly lack hydrated (water-bearing) minerals. The discovery strongly suggests that a large population of asteroids hurtling through the solar system may not be as dry as previously thought. The finding, published in Nature Astronomy, gives renewed push to the hypothesis that most if not all water on Earth may have arrived by way of asteroids during the planet’s tumultuous infancy.
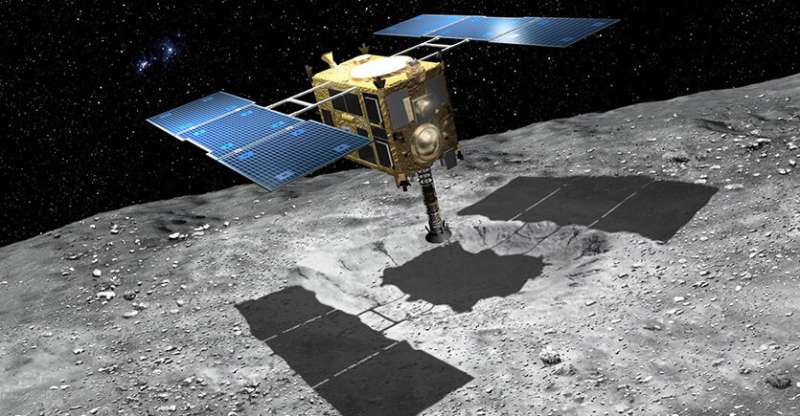
Zega and lead study author Shaofan Che, a postdoctoral fellow at the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, performed a detailed analysis of samples collected from asteroid Itokawa in 2005 by the Japanese Hayabusa mission and brought to Earth in 2010.
The study is the first to prove that the salt crystals originated on the asteroid’s parent body, ruling out any possibility they might have formed as a consequence of contamination after the sample reached Earth, a question that had plagued previous studies that found sodium chloride in meteorites of a similar origin.
“The grains look exactly like what you would see if you took table salt at home and placed it under an electron microscope,” said Tom Zega, the study’s senior author and a professor of planetary sciences at the UArizona Lunar and Planetary Laboratory. “They’re these nice, square crystals. It was funny, too, because we had many spirited group meeting conversations about them, because it was just so unreal.”
Zega said the samples represent a type of extraterrestrial rock known as an ordinary chondrite. Derived from so-called S-type asteroids such as Itokawa, this type makes up about 87% of meteorites collected on Earth. Very few of them have been found to contain water-bearing minerals.

“It has long been thought that ordinary chondrites are an unlikely source of water on Earth,” said Zega, who is the director of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory’s Kuiper Materials Imaging & Characterization Facility. “Our discovery of sodium chloride tells us this asteroid population could harbor much more water than we thought.”
Today, scientists largely agree that Earth, along with other rocky planets such as Venus and Mars, formed in the inner region of the roiling, swirling cloud of gas and dust around the young sun, known as the solar nebula, where temperatures were very high—too high for water vapor to condense from the gas, according to Che.
“In other words, the water here on Earth had to be delivered from the outer reaches of the solar nebula, where temperatures were much colder and allowed water to exist, most likely in the form of ice,” Che said. “The most likely scenario is that comets or another type of asteroid known as C-type asteroids, which resided farther out in the solar nebula, migrated inward and delivered their watery cargo by impacting the young Earth.”
The discovery that water could have been present in ordinary chondrites, and therefore been sourced from much closer to the sun than their “wetter” kin, has implications for any scenario attempting to explain the delivery of water to the early Earth.
The sample used in the study is a tiny dust particle spanning about 150 micrometers, or roughly twice the diameter of a human hair, from which the team cut a small section about 5 microns wide—just large enough to cover a single yeast cell—for the analysis.
Using a variety of techniques, Che was able to rule out that the sodium chloride was the result of contamination from sources such as human sweat, the sample preparation process or exposure to laboratory moisture.
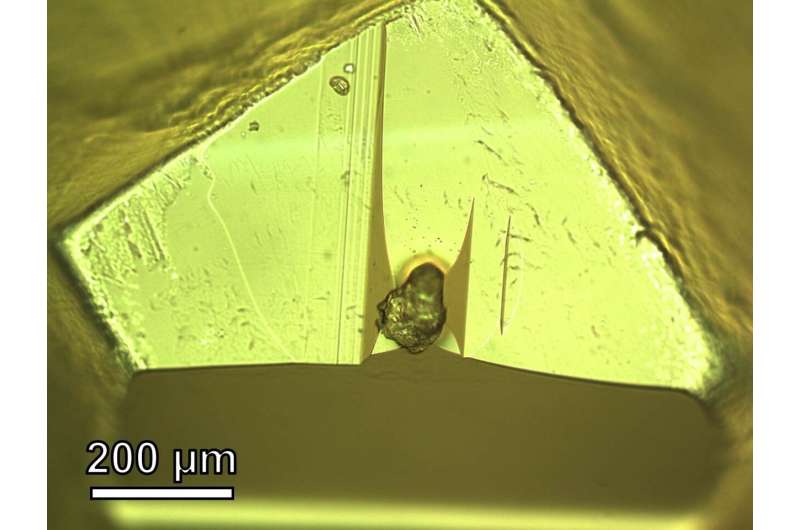
Because the sample had been stored for five years, the team took before and after photos and compared them. The photos showed that the distribution of sodium chloride grains inside the sample had not changed, ruling out the possibility that any of the grains were deposited into the sample during that time. In addition, Che performed a control experiment by treating a set of terrestrial rock samples the same as the Itokawa sample and examining them with an electron microscope.
“The terrestrial samples did not contain any sodium chloride, so that convinced us the salt in our sample is native to the asteroid Itokawa,” he said. “We ruled out every possible source of contamination.”
Zega said tons of extraterrestrial matter is raining down on Earth every day, but most of it burns up in the atmosphere and never makes it to the surface.
“You need a large enough rock to survive entry and deliver that water,” he said.
Previous work in the 1990s led by the late Michael Drake, a former director of the Lunar and Planetary Lab, proposed a mechanism by which water molecules in the early solar system could become trapped in asteroid minerals and even survive an impact on Earth.
“Those studies suggest several oceans worth of water could be delivered just by this mechanism,” Zega said. “If it now turns out that the most common asteroids may be much ‘wetter’ than we thought, that will make the water delivery hypothesis by asteroids even more plausible.”

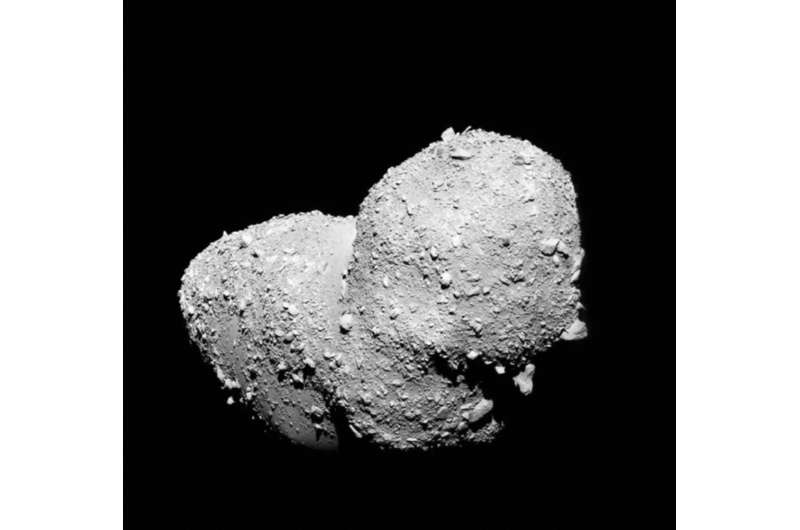
Itokawa is a peanut-shaped near-Earth asteroid about 2,000 feet long and 750 feet in diameter, and is believed to have broken off from a much larger parent body. According to Che and Zega, it is conceivable that frozen water and frozen hydrogen chloride could have accumulated there, and that naturally occurring decay of radioactive elements and frequent bombardment by meteorites during the solar system’s early days could have provided enough heat to sustain hydrothermal processes involving liquid water. Ultimately, the parent body would have succumbed to the pummeling and broken up into smaller fragments, leading to the formation of Itokawa.
“Once these ingredients come together to form asteroids, there is a potential for liquid water to form,” Zega said. “And once you have liquids form, you can think of them as occupying cavities in the asteroid, and potentially do water chemistry.”
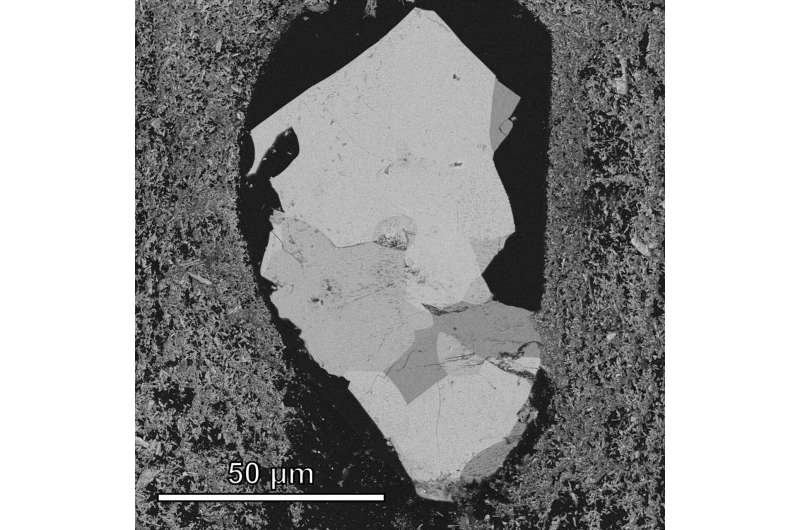
The evidence pointing at the salt crystals in the Itokawa sample as being there since the beginning of the solar system does not end here, however. The researchers found a vein of plagioclase, a sodium-rich silicate mineral, running through the sample, enriched with sodium chloride.
“When we see such alteration veins in terrestrial samples, we know they formed by aqueous alteration, which means it must involve water,” Che said. “The fact that we see that texture associated with sodium and chlorine is another strong piece of evidence that this happened on the asteroid as water was coursing through this sodium-bearing silicate.”
More information:
Shaofan Che et al, Hydrothermal fluid activity on asteroid Itokawa, Nature Astronomy (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41550-023-02012-x
Citation:
Pass the salt: This space rock holds clues as to how Earth got its water (2023, June 13)
retrieved 13 June 2023
from https://phys.org/news/2023-06-salt-space-clues-earth.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
For all the latest Science News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

