NASA’s IXPE gets an X-ray view of the famous Crab Nebula | Digital Trends
A NASA X-ray instrument has provided a new view of one of astronomy’s most beautiful objects, the Crab Nebula. The Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer or IXPE observatory was launched in December 2021 and is currently in orbit around the Earth from where it observes X-rays sources such as black holes and pulsars.
Although X-ray astronomy is an important way for scientists to learn about the cosmos, it’s not something that the public hears about so often because its results tend to be hard to convey visually. But recent results with IXPE show how an X-ray view of the universe can pick out fascinating features which would be invisible in other wavelengths.
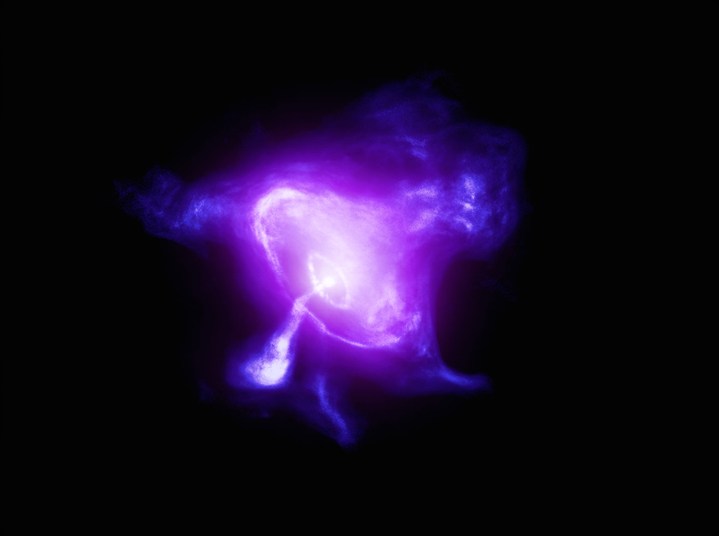
The Crab Nebula is the remnant of a supernova that exploded 6,500 light-years away from Earth, first observed by Chinese astronomers in 1054. When seen in the visible light wavelength, such as in images from the Hubble Space Telescope, it appears as a cloud of glowing dust and gas with delicate shapes formed by the supernova explosion.
But when seen in the X-ray wavelength, the nebula looks quite different. IXPE observed the nebula’s magnetic field, the shape of which is indicated by the orange lines in the image below.
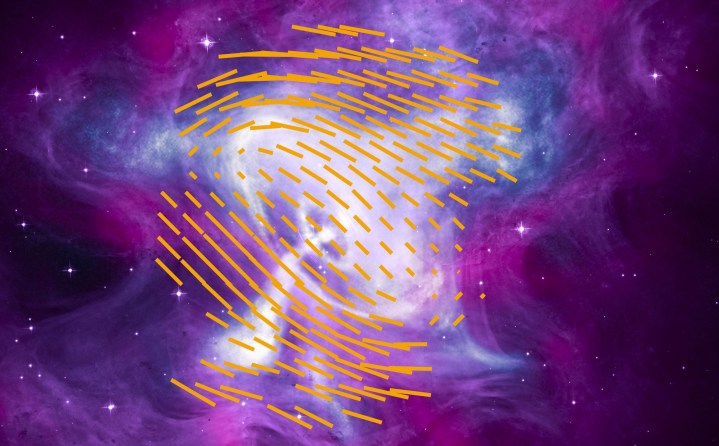

Previous observations of the Crab Nebula included looking at it using another X-ray instrument, the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which was able to pick out the jets which formed through the gas and dust. But IXPE was able to get a different view of the nebula by looking at polarization, which shows the direction of electromagnetic fields. It showed that some areas of the nebula are polarized differently from others, and was able to detect X-rays coming from the pulsar at the heart of the nebula.
“The Crab is one of the most-studied high-energy astrophysical objects in the sky. So it is extremely exciting that we could learn something new about this system by looking through IXPE’s ‘polarized lenses,’” said one of the researchers, Michela Negro of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, in a statement.
The research is published in the journal Nature Astronomy.
Editors’ Recommendations
For all the latest Technology News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

