NASA finds each state has its own climatic threshold for flu outbreaks
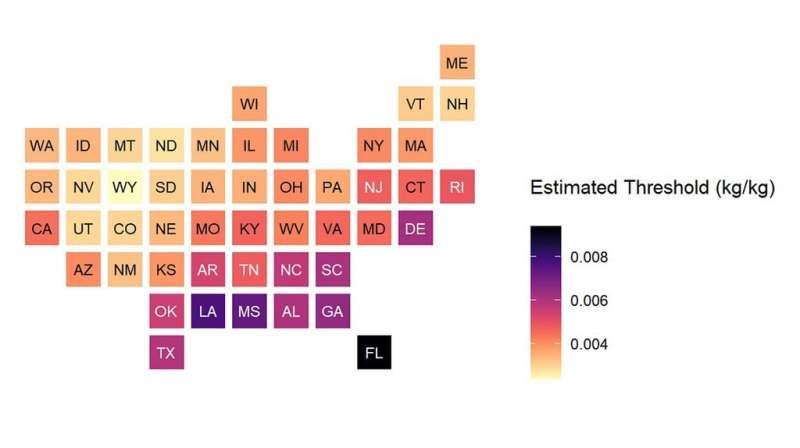
What triggers an outbreak of the influenza virus? A new study of the flu in the 48 contiguous U.S. states, using data from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) on NASA’s Aqua satellite, has found that the answer is closely tied to local weather—specifically, to low humidity—and varies from state to state.
Average humidity varies widely across the United States, but even in the most humid states, it begins to drop as winter approaches. Researchers at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California and the University of Southern California correlated AIRS measurements of water vapor in the lower atmosphere with flu case estimates for each week from 2003 to 2015. The researchers found that in each state, there is a specific level of low humidity that may signal a flu outbreak is imminent. When this threshold is crossed each year, a large increase in flu cases follows within two or three weeks, on average.
These threshold levels of low humidity closely parallel each state’s average climate. Although all 48 states have different thresholds, states with humid climates, such as those in the Southeast, have higher threshold values than arid states, including those in the West and Southwest.
The study wasn’t designed to answer why lower humidity leads to flu outbreaks.
E. Serman et al, Spatial Variation in Humidity and the Onset of Seasonal Influenza Across the Contiguous United States, GeoHealth (2021). DOI: 10.1029/2021GH000469
Citation:
NASA finds each state has its own climatic threshold for flu outbreaks (2022, March 4)
retrieved 4 March 2022
from https://phys.org/news/2022-03-nasa-state-climatic-threshold-flu.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
For all the latest Science News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

