Multiple-model GWAS identifies optimal allelic combinations of quantitative trait loci for malic acid in tomato
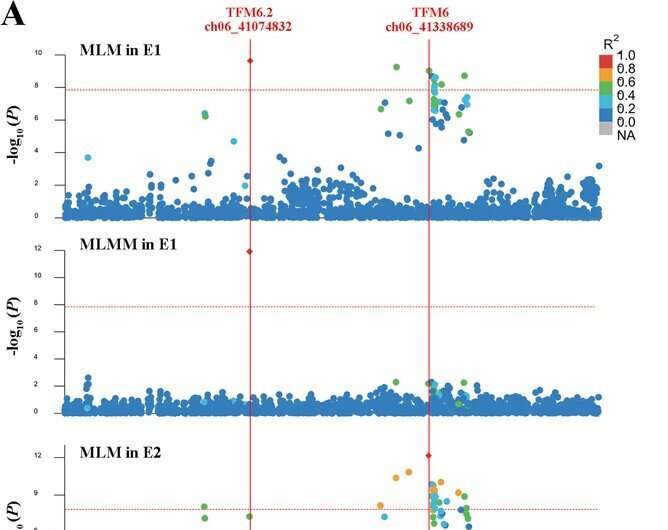
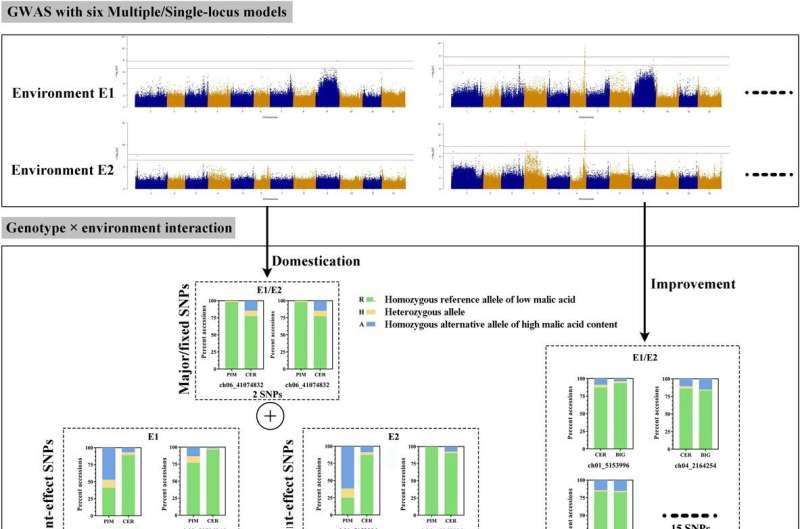
A study published in the journal Horticulture Research sought to identify loci and decipher the polygenic architecture of malic acid content in tomato fruit. The authors carried out a GWAS using six milestone models with two-environment repeats. A series of associated SNP variations were identified from GWAS, and 15 high-confidence annotated genes were obtained based on the lead SNPs and the malic acid accumulation.
The optimal allelic combination of the 15 loci was presented for tastier tomato. The genetic parameters of population-differentiation were employed to identify potential selective sweep signals on malic acid during domestication and improvement.
The authors identified natural variations underlying malic acid in tomato with multiple-model GWAS. This study will provide new genetic insights into how tomato malic acid content evolved during breeding and optional QTL combinations for higher malic acid in tomato.
More information:
Wenxian Gai et al, Multiple-model GWAS identifies optimal allelic combinations of quantitative trait loci for malic acid in tomato, Horticulture Research (2023). DOI: 10.1093/hr/uhad021
Citation:
Multiple-model GWAS identifies optimal allelic combinations of quantitative trait loci for malic acid in tomato (2023, April 24)
retrieved 25 April 2023
from https://phys.org/news/2023-04-multiple-model-gwas-optimal-allelic-combinations.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
For all the latest Science News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

