M87 data from Event Horizon Telescope rules out the likelihood of axion particles in a specific mass range
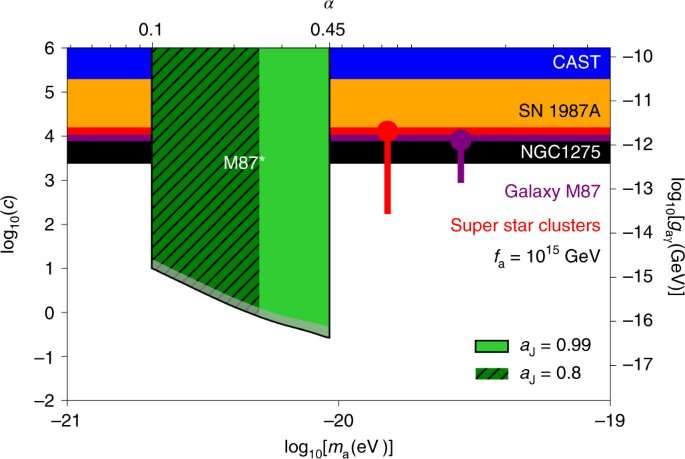
A team of researchers affiliated with multiple institutions in China and two in Germany has found that data from the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) rules out the likelihood of axion particles in a specific mass range around the black hole M87. In their paper published in the journal Nature Astronomy, the group describes their analysis of data recently obtained from the EHT and what it showed about time-varying changes in the polarization’s direction.
Axions were first proposed back in the 1970s to explain why there is so little antimatter in the universe. The particles are also theorized to be part of dark matter. Unfortunately, no one has been able to prove they exist. Instead, physicists continue to look for circumstantial evidence of their existence. In this new effort, the researchers have looked into another theoretical idea—one that suggests axions should build up in clouds around black holes. Scientists had not been able to test this theory until recently because they have not had images made of the polarized light emitted from a black hole. That changed last year when the EHT (a network of radio telescopes across the globe) captured images of the black hole M87 and released them for use by other researchers.
Theory suggests that axions in a cloud around a black hole should alter the polarization of light coming from that part of the cloud—there should be a wobble. The researchers with this new effort analyzed the data from EHT, looking for such a wobble. But to do that, they had to filter out other material that could also contribute to a wobble. Once that was done, they found that the remaining bit of wobble ruled out the possibility of ultralightweight axions in the cloud. The techniques they used could also be applied to the search for axion-like particles around other black holes, such as the one at the center of the Milky Way galaxy—which just happens to be one of the upcoming targets of the EHT.
Using a Floquet quantum detector to constrain axion-like dark matter
Yifan Chen et al, Stringent axion constraints with Event Horizon Telescope polarimetric measurements of M87⋆, Nature Astronomy (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41550-022-01620-3
© 2022 Science X Network
Citation:
M87 data from Event Horizon Telescope rules out the likelihood of axion particles in a specific mass range (2022, March 18)
retrieved 18 March 2022
from https://phys.org/news/2022-03-m87-event-horizon-telescope-likelihood.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
For all the latest Science News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

