Importance of Wolbachia-mediated biocontrol to reduce dengue in Bangladesh and other dengue-endemic developing countries
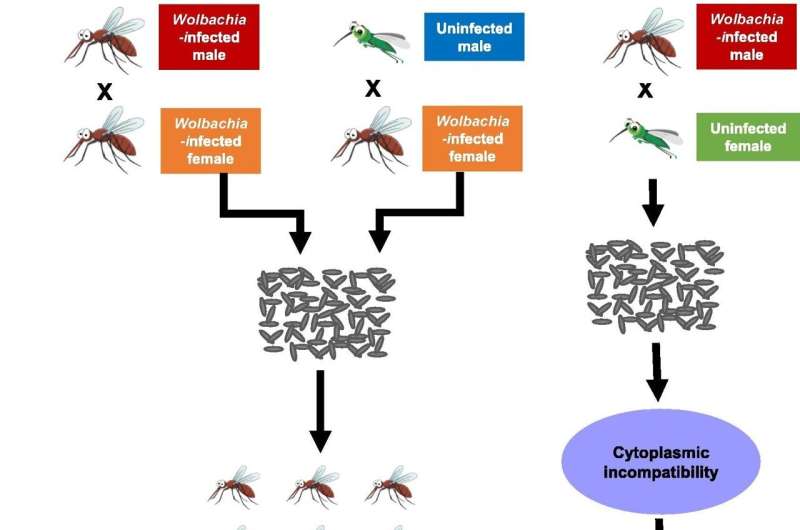
Mosquito-borne diseases, particularly dengue and chikungunya have become global threats, infecting millions of people worldwide, including developing countries of Southeast Asia and Latin America. Bangladesh, like many other developing countries, is experiencing frequent dengue outbreaks. This article, therefore, critically discusses the current status of dengue disease, vector control approaches, and the need for Wolbachia-mediated intervention in Bangladesh and other dengue-endemic developing countries.
Relevant literature was searched from major databases and search engines such as PubMed, BanglaJol, World Health Organization (WHO)/European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) and Google Scholar. Considering the selection criteria, search strategies finally involved 55 related literature for further investigation.
Findings showed that current vector control strategies could not render protection for an extended period, and the disease burden of arboviruses is increasing. The impoverished outbreak preparedness, urbanization, climate change, and less efficacy of existing control methods have made people susceptible to vector-borne diseases.
Hence, Wolbachia, a naturally occurring endosymbiont of many mosquito species that can potentially limit virus transmission through several host genetic alterations, would be a potential alternative for dengue prevention.
The authors also critically discuss the challenges and prospects of Wolbachia-based dengue control in developing countries. The evidence supporting the efficacy and safety of this intervention and its mechanism have also been elucidated.
Empirical evidence suggests that this introgression method could be an eco-friendly and long-lasting dengue control method. This review helps policymakers and health experts devise a scheme of Wolbachia-based dengue control that can control mosquito-borne diseases, particularly dengue in Bangladesh and other developing countries.
The research is published in the journal Biosafety and Health.
More information:
Abdullah Al Noman et al, Importance of Wolbachia-mediated biocontrol to reduce dengue in Bangladesh and other dengue-endemic developing countries, Biosafety and Health (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.03.003
Provided by
Compuscript Ltd
Citation:
Importance of Wolbachia-mediated biocontrol to reduce dengue in Bangladesh and other dengue-endemic developing countries (2023, June 9)
retrieved 9 June 2023
from https://phys.org/news/2023-06-importance-wolbachia-mediated-biocontrol-dengue-bangladesh.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
For all the latest Science News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

