Efficient uptake of uranium(VI) realized by layered manganese thiophosphite intercalated with ammonium
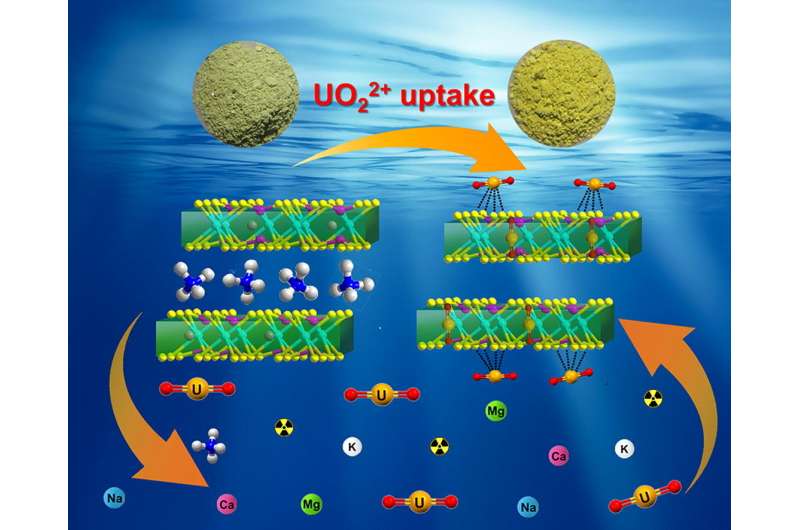
With the rapid development of nuclear power worldwide, the demand for uranium continues to increase. As a consequence, large quantities of uranium-containing wastewater are generated throughout the nuclear fuel cycle as well as during spent fuel reprocessing. Uranium (U) is highly chemical toxic and strongly carcinogenic to the living system. Therefore, it is important to develop materials that can capture U(VI) ions efficiently and selectively.
In a study published in Chemical Engineering Journal, Prof. Feng Meiling from Prof. Huang Xiaoying’s research group at the Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported a layered manganese thiophosphate intercalated with NH4+, namely (NH4)0.48Mn0.76PS3·H2O (N-MPS), which could rapidly and selectively separate U(VI) from complex solutions. This is the first report of an intercalation compound of manganese thiophosphite (MnPS3) to enrich U(VI) efficiently.
The researchers prepared N-MPS by immersing a quantity of MnPS3 in 2 mol/L NH4Cl aqueous solution and stirring at room temperature for 24 hours. The prepared N-MPS shows good pH durability (2.8–12.2) and β/γ-ray irradiation resistance (100–200 KGy).
Moreover, they found that N-MPS exhibits an outstanding capacity (much higher than that of some reported superior sulfide adsorbents), fast kinetics, and superb selectivity towards U(VI).
In particular, the obtained distribution coefficient values in contaminated tap water and lake water are up to 2.23 × 104 mL/g.
Importantly, the adsorbed U(VI) could be eluted by a mild and eco-friendly method for the recovery of uranium and regeneration of adsorbent for at least five cycles.
Using various characterizations (Raman, XPS, Zeta potential and EXAFS) and batch adsorption experiments, the researchers revealed that the adsorption mechanism of N-MPS for U(VI) is the synergy of ion exchange and surface adsorption.
This study not only shows that intercalated metal sulfides have good application potential for highly efficient separation of U(VI) from wastewater, but also paves the way for developing new high-performance adsorbents by intercalation.
Highly selective recovery of lanthanides via layered vanadate with acid and radiation resistance
Xi Zeng et al, Efficient uptake of uranium(VI) by a layered manganese thiophosphite intercalated with NH4+, Chemical Engineering Journal (2021). DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.132474
Citation:
Efficient uptake of uranium(VI) realized by layered manganese thiophosphite intercalated with ammonium (2021, October 20)
retrieved 20 October 2021
from https://phys.org/news/2021-10-efficient-uptake-uraniumvi-layered-manganese.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
For all the latest Science News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

