Development of a versatile method to synthesize functional mRNAs with diverse 5′ cap structures
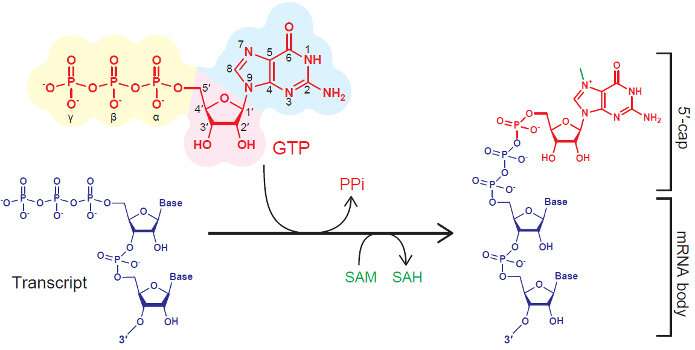
Synthetic mRNAs are explored rigorously for their potential as an effective genetic vector for basic research and clinical applications. Natural mRNAs have a structure on their leading (5′) ends—called the 5′ cap—that regulates their stability and translational activity. As such, there is a tremendous effort to devise new methods to chemically modify and generate functional 5′ cap structures.
In this study, published in Nucleic Acids Research on February 3, 2023, the research group reported a simple and efficient method for synthesizing functional mRNAs by modifying the 5′ cap using an enzyme from the vaccinia virus.
The team exploited the ability of this enzyme to introduce various GTP analogs at the 5′ end of mRNAs and showed that mRNAs with 5′ cap modifications generated by this enzyme exhibit different translational activity. In particular, some modified mRNAs have improved translation efficiency or contain chemical groups for incorporating functional molecules, such as azido-modified GTP analogs, to attach desired molecules like fluorescent dyes or biotin, thus expanding the functionality of the modified mRNAs.
This novel method for modifying 5′ mRNA caps provides biologists with a versatile tool in their molecular biology toolbox to advance basic biomedical research and develop new RNA therapeutics.
More information:
Hirohisa Ohno et al, Versatile strategy using vaccinia virus-capping enzyme to synthesize functional 5′ cap-modified mRNAs, Nucleic Acids Research (2023). DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkad019
Citation:
Development of a versatile method to synthesize functional mRNAs with diverse 5′ cap structures (2023, February 3)
retrieved 3 February 2023
from https://phys.org/news/2023-02-versatile-method-functional-mrnas-diverse.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
For all the latest Science News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

