Chemically bonded multi-nanolayer aerogel for thermal superinsulation
Thermal superinsulation materials with low thermal conductivities are essential for thermal insulation and protection under extreme conditions. These materials are particularly required in fields including deep-space exploration, aerospace, mechanical, and thermal power engineering, which need exceptional insulation and reliability.
Inorganic aerogels have exhibited many superior characteristics such as ultralight weight, high deformability, excellent fire/corrosion resistance and low thermal conductivity, demonstrating promise in thermal insulators.
However, inorganic aerogels are still plagued by a tradeoff between their mechanical and thermal properties, presenting a key roadblock to further explore their functionality. Although enhancement in mechanical or thermal properties has been well studied in inorganic aerogels, there is still a lack of efficient synergistic strategies to solve this typical tradeoff.
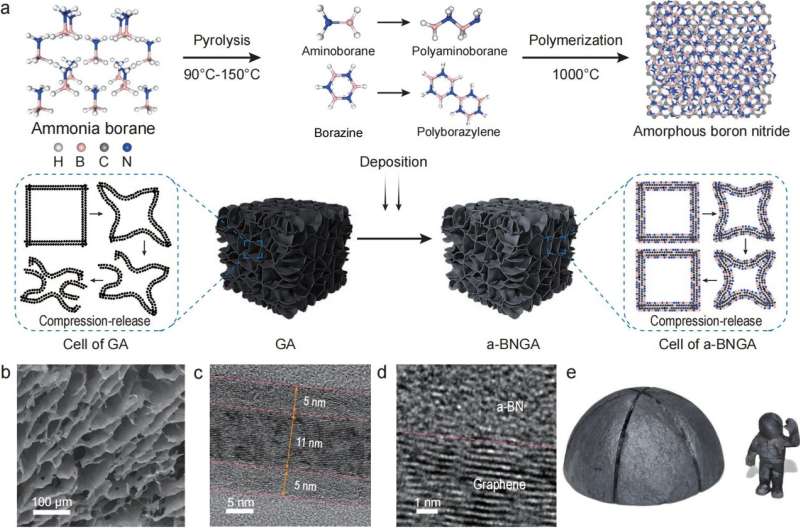
In a new research article published in the National Science Review, researchers at Harbin Institute of Technology and Southeast University present a chemically bonded multi-nanolayer design and synthesis of a graphene/amorphous boron nitride aerogel (a-BNGA) to simultaneously enhance the mechanical and thermal properties.
In contrast to previous works, the graphene framework is uniformly deposited by a-BN nanolayer on both sides, forming a chemically bonded multi-nanolayer structure. It was found that the chemically bonded interfaces tightly anchor the uniform a-BN jacket onto the graphene skeleton, which acts via a tendon-like mechanism, ensuring a synergistic deformation and load transfer in the framework.
In addition, a-BN nanolayer can increase the elastic stiffness of cell walls endows a desirable bending moment distribution, realizing a coupled toughening effect to enhance the structural resilience.
The resulting a-BNGA features an ultralow density with ultrahigh flexibility (elastic compressive strain up to 99%, elastic bending strain up to 90%) and exceptional thermal stability (almost no strength degradation after sharp thermal shocks). The researchers demonstrate the flexible deformability by the fold and unfold process of an aerogel flower in human hand.
Notably, the a-BN nanolayer in aerogel, which exceeds 20% in volume, is mechanically crucial but thermally inactive-an ideal state for thermal insulation materials. The solid conduction and radiation contributions, which together make up the apparent thermal conductivity of material in vacuum. Benefiting from the scarcity of effective conduction paths by low density and the additional phonon scattering by interface, solid conduction can be effectively inhibited.
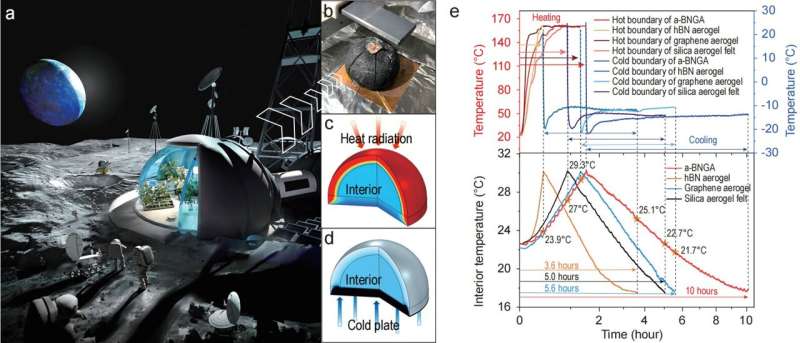
Furthermore, graphene can be used as an infrared absorber to reduce the radiative thermal transport. The researchers experimentally proved this aerogel with record-low thermal conductivity in vacuum among freestanding solid materials to date. In addition, they designed a lunar base model working in high-vacuum to showcase the thermal superinsulation capabilities of aerogel in extraterrestrial exploration application.
“We achieve a combination of exceptional mechanical and thermal properties of inorganic aerogel and defining a robust material system for thermal superinsulation at extreme conditions, such as lunar and Mars bases, satellites and spacecrafts,” Prof. Xiang Xu said, “This kind of material and structural design may also provide opportunities for inorganic aerogels to endow other unique functions.”
More information:
Hongxuan Yu et al, Chemically bonded multi-nanolayer inorganic aerogel with a record-low thermal conductivity in a vacuum, National Science Review (2023). DOI: 10.1093/nsr/nwad129
Citation:
Chemically bonded multi-nanolayer aerogel for thermal superinsulation (2023, July 19)
retrieved 19 July 2023
from https://phys.org/news/2023-07-chemically-bonded-multi-nanolayer-aerogel-thermal.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
For all the latest Science News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

