Analyzing a new material that promises faster, higher resolution displays
A new material is set to provide us with faster and higher resolution displays. Hokkaido University researchers explain what makes this material so special, opening the door to its application and further development.
All displays consist of a lattice of tiny dots of light, called pixels, the brightness of which can be individually controlled. The total number of pixels—and therefore, the resolution and display size—is limited by how many of these pixels can be addressed within a given fraction of a second. Therefore, display manufacturers try, in the pixel control units, to use materials that exhibit a very high “electron mobility,” which is a measure for how quickly current will start to flow through a control unit as a response to voltage being applied—and thus, how quick the pixel is.
A new material called ITZO (for its constituent elements indium, tin, zinc and oxygen) promises to be up to seven times faster than the current state-of-the-art material. However, it has not been clear where this improvement comes from, hampering its adoption for industrial applications.
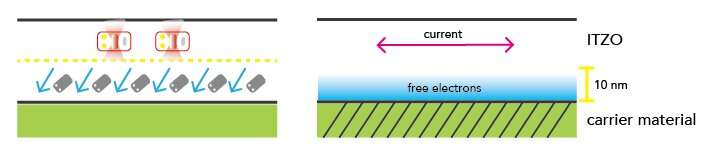
Hokkaido University material scientist Hiromichi Ohta and his team used their unique measurement technique to clarify this point. In their recent paper published in the journal ACS Applied Electronic Materials, they showed that the higher electron mobility results from the unusual fact that in ITZO films of sufficient thickness, free charges accumulate at the interface with the carrier material and thus enable passing-through electrons to travel through the bulk of the material unhindered.
The unique ability comes down to a very simple formula: The electron mobility is proportional to the free travel time of the charge carriers—electrons in this case—divided by their effective mass. And while the measurement of the electron mobility itself is a relatively standard technique, effective mass and free travel time cannot be measured as easily, and therefore it is difficult to tell what factor is responsible for the electron mobility.
But by measuring how the electric field inside the material changes in response to an applied magnetic field as well as to a temperature gradient, Ohta’s team could deduce the effective mass of the electrons—and then calculate the free travel time as well. It turns out that both the effective mass is significantly smaller than in current state-of-the-art materials and the free travel time is much higher and, therefore, both factors contribute to the higher electron mobility. In addition, by observing how their results depend on the thickness of the ITZO material, they could deduce how the interface and bulk of the material contribute to these effects.
Ohta explains the significance of this analysis: “Using the knowledge we gained from this study, we may in the future design other transparent oxide semiconductor thin-film transistors with different chemical compositions that exhibit even better electron mobility properties.” Thus, this study is a major step toward the next generation of ultra high-resolution displays.
An expressway for electrons in oxide heterostructures
Hui Yang et al, Thermopower Modulation Analyses of High-Mobility Transparent Amorphous Oxide Semiconductor Thin-Film Transistors, ACS Applied Electronic Materials (2022). DOI: 10.1021/acsaelm.2c01210
Citation:
Analyzing a new material that promises faster, higher resolution displays (2022, October 14)
retrieved 15 October 2022
from https://phys.org/news/2022-10-material-faster-higher-resolution.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
For all the latest Science News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

