Research team reveals surprising findings on cyclic material fatigue in amorphous materials
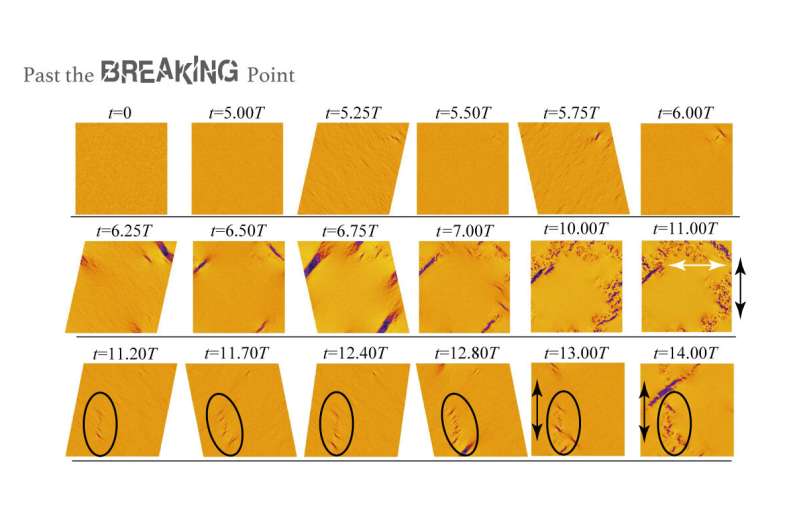
Researchers at The University of Tokyo have shown that for amorphous materials, cyclic material fatigue can begin to fracture at the same level of stress as fractures due to constant loading. By using computer simulations, the team was able to distinguish four distinct failure modes. This work could improve the lifetime of industrial machinery.
Damage to industrial parts is expensive, results in delays, and may be unsafe to plant workers. But now, the scientists from Japan have simulated fracture initiated in materials that share a particular physical characteristic and are widely used across domestic, industrial and scientific applications. Their work, published in Communications Materials, showed surprising results that may help prevent damage to industrial parts.
If you’ve ever been bored in a meeting and tried playing with a metal paperclip to pass the time, you may have noticed something surprising. Although the paperclip starts flexible and returns to its original shape several times, it may suddenly snap after enough cycles. This is an example of “fatigue,” in which cracks and defects build up as an object is subjected to cyclic loading and unloading of stress. Material fatigue is a significant concern in many industrial applications, and especially for machine or airplane parts that experience many cycles of stress, and for which a sudden failure could be catastrophic. As a result, obtaining a better understanding of the underlying process of material fatigue could yield significant benefits, especially for non-crystalline materials.
The team of researchers at the Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo, studied the physical mechanisms of low-cycle fatigue fracture in the case of amorphous solids, such as glass or plastics, using computer simulations. For crystalline materials, it has been shown that pre-existing defects and grain boundaries can initiate a fracture because of fatigue.
However, the corresponding mechanism in amorphous materials is not well understood. While it seems intuitive that the stress required for a fracture to occur is much smaller for cyclic stresses compared with constant stress, this was not what the scientists found. “Contrary to the common belief, we showed that the critical strain in disorder materials that corresponds with the onset of irreversible deformation is the same for both fatigue and monotonic fractures,” says co-author Yuji Kurotani.
This is because for ordinary amorphous systems, higher density leads to more elasticity and slower dynamics. This density dependence of mechanical properties couples the shear deformation with density fluctuations. The cyclic shear can then amplify density fluctuations until the sample breaks via cavitation, in which voids are produced.
“This situation is like a crowded train,” says co-author Hajime Tanaka. “Dynamic and elastic asymmetries with respect to density changes can lead to a link between shear deformation and density fluctuations.” These authors mention that these results should be confirmed with experiments, which would also help material scientists better understand the initiation of fractures.
Deformation fingerprints will help researchers identify, design better metallic materials
Fatigue fracture mechanism of amorphous materials from a density-based coarse-grained model, Communications Materials (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s43246-022-00293-9
Citation:
Research team reveals surprising findings on cyclic material fatigue in amorphous materials (2022, October 11)
retrieved 11 October 2022
from https://phys.org/news/2022-10-team-reveals-cyclic-material-fatigue.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
For all the latest Science News Click Here
For the latest news and updates, follow us on Google News.

